Table of Contents
- What is a car paint thickness gauge?
- Three paint thickness measurement principles
- Magnetic PTG for steel
- Eddy current PTG (electromagnetic)
- Ultrasonic PTG
- Why is it important to measure paint thickness?
- How to take the paint thickness measurement
- 1. Prepare your car’s surface
- 2. Calibrate the device
- 3. Position the gauge
- 4. Measure the paint thickness
- 5. Check and analyze the results
- What are good paint depth results?
- When to use a paint thickness gauge?
How to use a car paint thickness gauge
When buying a car, many still consider the paint a matter of aesthetics. However, the primary function of car paint goes beyond mere aesthetics.
For one thing, the paint on a car also acts as a shield against environmental elements, such as sunlight, moisture, or road debris. Over time, this protective layer can wear off or become damaged, making your vehicle vulnerable to corrosion and diminishing its value.
That’s why using a car paint thickness gauge can be highly beneficial to car owners and buyers.
Looks can be deceiving!
Don't risk your safety - check it with carVertical first
What is a car paint thickness gauge?
A car paint thickness gauge (PTG), also known as a paint meter, is a device that allows you to measure the thickness of the paint or coating on your vehicle’s surface.
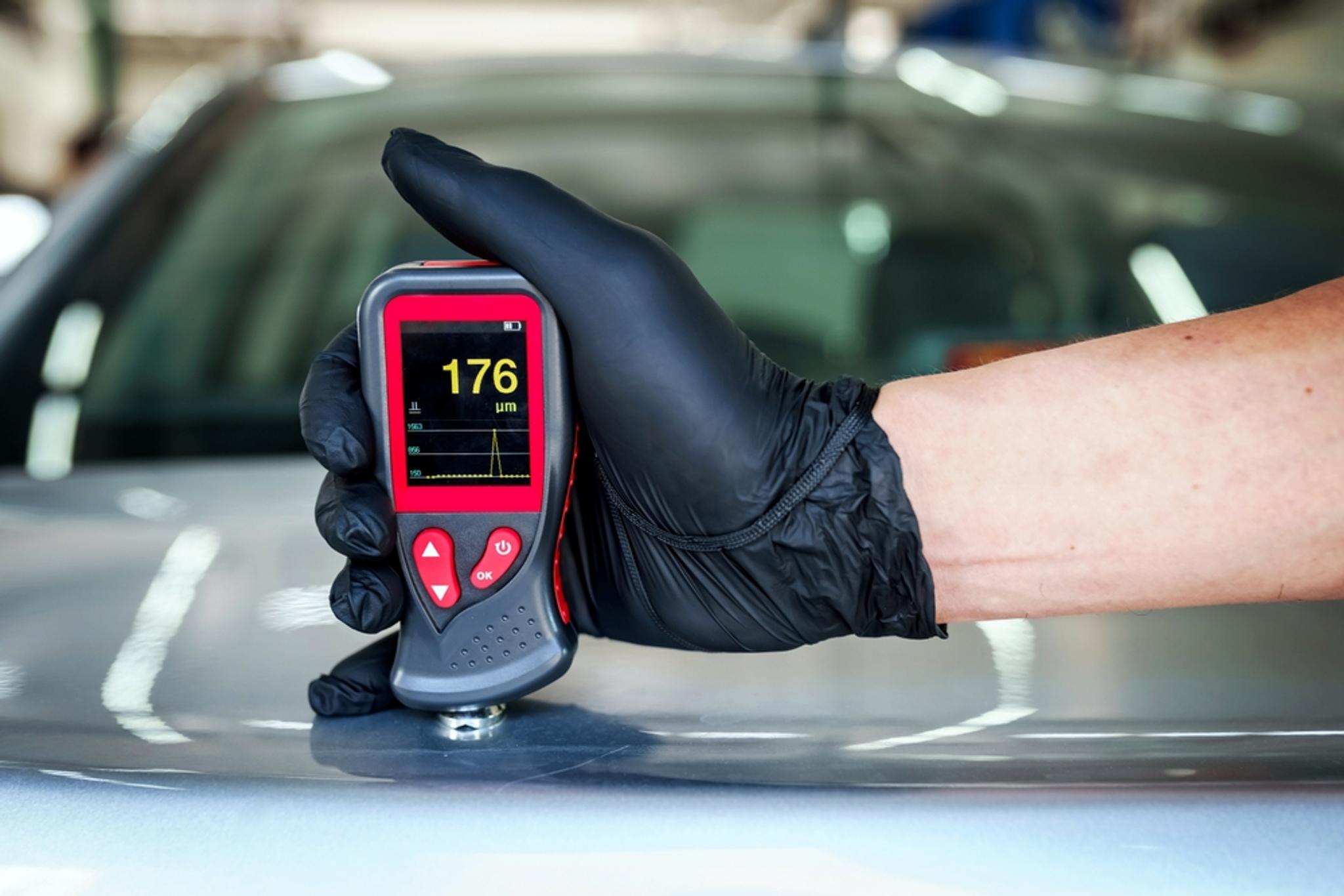

Car enthusiasts and professionals use this car diagnostic tool to evaluate the condition of a car’s paintwork, which helps to identify inconsistencies or abnormalities. For example, you can use it to:
- Determine if the paint thickness is within the manufacturer’s specifications
- Detect repainted areas
Typically, measurements are provided in microns (µm – one millionth of a meter) or millimeters (mm – one thousandth of an inch).
Three paint thickness measurement principles
Depending on the type of your PTG, paint thickness measurement techniques can vary slightly.
Typically, a PTG consists of a probe or a sensor and works based on the principles of magnetic and electromagnetic induction as well as ultrasonic principles.
Magnetic PTG for steel
You can use a PTG that works using magnetism to measure paint thickness on steel substrates. This specific paint thickness gauge type operates based on the interaction between the gauge’s probe and the magnetic field created when you place the probe on the steel surface.
The presence of paint or coating layer then affects the magnetic field’s interaction with the metal. This causes changes in the magnetic field that a PTG converts into readings, and the results get displayed on the screen.
Eddy current PTG (electromagnetic)
A paint thickness gauge that operates based on the eddy current principle is used for measuring paint thickness on non-magnetic substrates such as aluminum or non-ferrous metals.
In general, the process is similar to the other two principles. Once you place the probe on the car’s surface, the device generates an electromagnetic field.
The electromagnetic field, interacting with the metallic substrate beneath the paint layer, induces eddy currents (swirling electric currents) that cause changes to the field. These changes are directly related to the thickness of the paint or coating layer on top of a metal substrate, therefore, the device converts them into paint thickness readings.
Ultrasonic PTG
Last but not least, a PTG that’s based on ultrasonics uses sound waves to measure paint thickness on various materials.
The device emits ultrasonic sound waves toward the surface of a vehicle. These waves then travel through the paint layer and reflect back from the surface.
In this case, a paint thickness gauge measures the time it takes for the sound waves to travel through the paint layer and return (which is determined by the paint thickness). A PTG converts the measured time into paint thickness readings that you can see on the screen.
Why is it important to measure paint thickness?

Paint thickness is a crucial indicator of the vehicle’s overall condition, allowing car owners to take timely action, ultimately preserving the vehicle’s value and aesthetics.
There are several reasons why measuring paint thickness can benefit you, including:
- Assessing the wear and tear. Over time, paint naturally wears down due to various external factors. Measuring paint thickness can help you identify the level of wear and tear (thin spots, paint fading, etc.) and signal that it’s time for restoration work.
- Preventing potential damage. Measuring car paint thickness is crucial for the long-term preservation of your car’s appearance and protection against corrosion. Maintaining the appropriate paint thickness level can help you address potential issues and take the necessary steps early.
- Identifying hidden damage. This part is especially important for those buying a used car. Sometimes, a thick layer of paint can indicate an attempt to hide underlying damage, such as rust or bodywork repairs. Identifying discrepancies can encourage further investigation, enabling you to make more informed purchase decisions.
- Detecting prior repairs. This information is valuable to every potential used car owner who wants to understand a vehicle’s history. Significant paint thickness variations between different car parts can indicate previous repairs or modifications.
- Evaluating paintwork quality. Whether you like to fix things yourself or want to check how well professionals did their job, a paint thickness gauge can help you ensure that the paintwork quality meets the required standards.
- Preserving resale value. A PTG can help car owners protect their vehicles and positively influence their car’s resale value when it’s time to sell. A well-maintained vehicle with a healthy paint thickness demonstrates care and attention to detail, which can significantly impact a buyer’s decisions.
How to take the paint thickness measurement
If you want to measure the paint thickness correctly, simply touching your vehicle’s surface with a PTG is usually not enough. You have to complete a couple of easy steps to get accurate and reliable results.

1. Prepare your car’s surface
You don’t need to wash your whole car for it, but cleaning the area you want to measure is highly recommended.
Make sure there’s no dust, dirt, rust, loose paint, or anything else that can impact a PTG’s readings in one way or another. There’s no need to use any special cleaning products for that – a clean cloth will work most of the time.
2. Calibrate the device
Calibrating your paint thickness gauge before every use is not necessary, yet it’s important to do it regularly or whenever the measuring conditions change to ensure the highest measurement accuracy.
The easiest way to do it is to check the manufacturer’s instructions and follow the steps on the screen. Typically, “calibration kits” are included in the package and come with various pieces of metal to simulate different substrates.
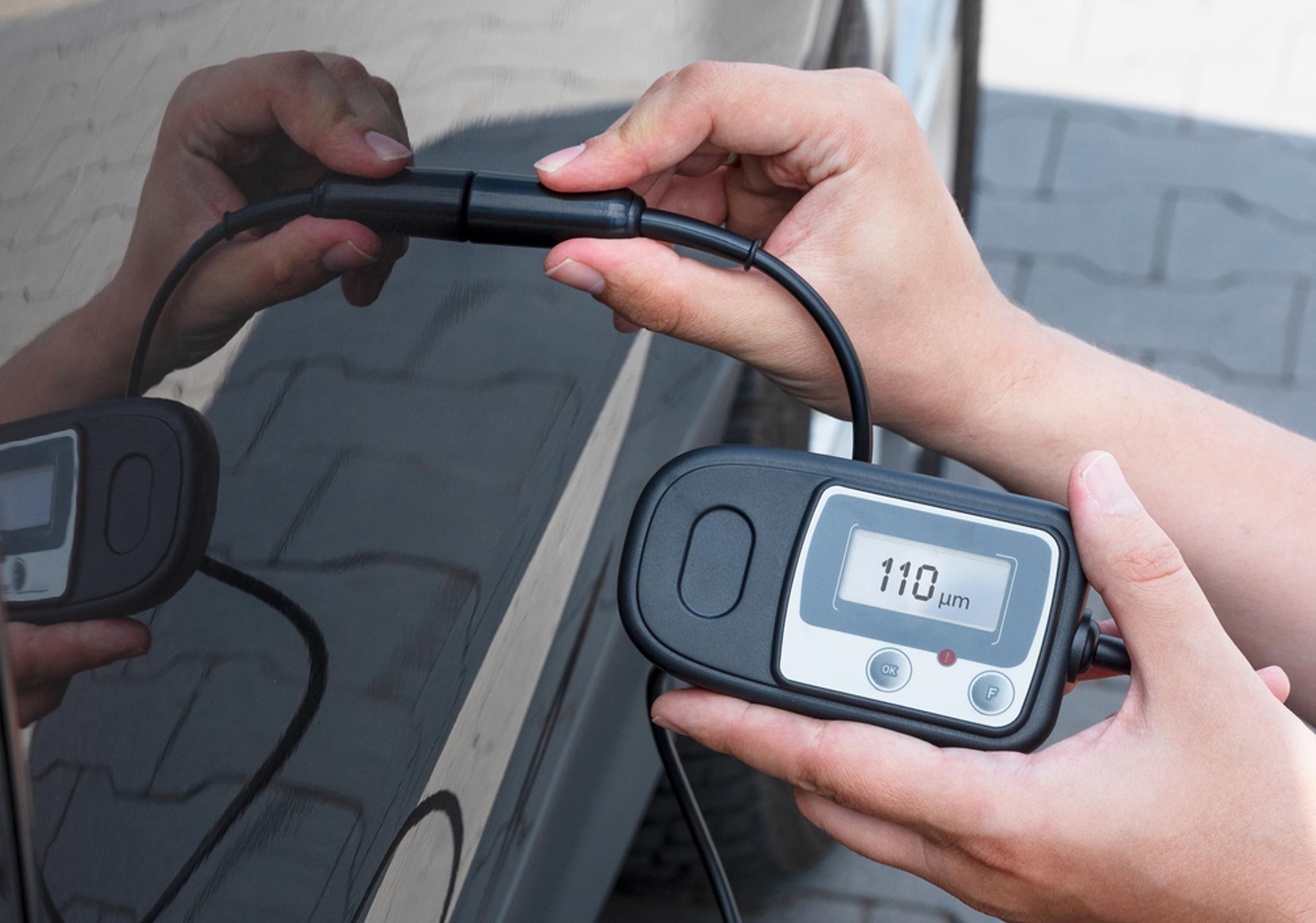
3. Position the gauge
Turn on the device, pick a unit of measurement (if required), and place the probe on the surface you want to measure. Ensure that the contact with the surface is firm – if necessary, apply a small amount of pressure on the gauge.
4. Measure the paint thickness
Press the measurement button or a trigger on the gauge to initiate the measurement. Hold the PTG steady and do not remove it until you see the readings on the screen.
5. Check and analyze the results
Shortly, you will be able to see the results of your measurements.
It’s recommended to take multiple measurements at different surface areas for the highest accuracy, ideally at representative areas of the vehicle (e.g., roof, trunk, doors, depending on the purpose of the measurement).
This will help you analyze the readings and understand the paint thickness distribution on your car’s surface.
What are good paint depth results?
Although there isn’t one universal number that defines “good” paint depth results, most factory paint jobs generally range from 100-180 microns (µm) or 4-7 mills on average.
It’s common to consider these guidelines:
- European cars – 100-150 microns (4-6 mills)
- American cars (USA) – 100-150 microns (4-6 mills)
- Japanese cars – 90-120 microns (3.5-4.7 mills)

However, even these numbers cannot be followed blindly, as the car paint thickness level can vary dramatically based on different factors, including:
- Car manufacturer – car paint thickness readings can vary not only between different manufacturers but also between different models from the same manufacturer. Each vehicle is unique.
- Price – it’s not uncommon for more expensive cars to have thicker layers of paint, while cheaper cars often have thinner ones.
- Car surface area – the whole car isn’t painted at once, and that’s one of the reasons why readings can vary depending on where you take the measurement. For example, harder-to-reach areas are typically painted first, thus going through overspray(s) later. Moreover, multiple sprayers often paint one car, which can result in overlapping, therefore, thicker paint.
- Paint color – since all colors have different opacity, some of them require heavier coats for better coverage.
- Application technique – factors such as spray gun settings, pattern, distance from the surface, and the number of coats applied can also impact the thickness of each paint layer.
- Substrate material – different materials of the vehicle’s surface (e.g., steel, aluminum, plastic) may require specific paint thickness to ensure durability and protection against external factors.
So if you’re looking for any particular number when measuring car paint thickness, it’s not really the right approach. What’s important here is consistency, or how much measurements vary across your vehicle.
If you notice areas of reduced thickness and the numbers show significant variations, you may want to investigate those differences.
When to use a paint thickness gauge?

You can benefit from using a paint thickness gauge in various situations, from restoration projects to evaluating the condition of the car you’re buying.
For instance, if you’re buying a used car and are not sure about its care history, you may want to measure the paint level on different panels. Again, higher readings can signal a repaint, meaning that the car was involved in some accident or the metals were rusty.
Another use case for a PTG is measuring the paint thickness before car detailing jobs. As they often involve cosmetic work, it’s important to know the paint levels before doing any corrections. It will allow you or auto detailers to determine if the car’s surface contains enough clear coat to do modifications safely.
Finally, it’s beneficial to check the quality of the paint job after it’s done. By using a paint thickness gauge to measure different panels, you can evaluate whether you/auto detailers did a good job.

Check your VIN
Avoid costly problems by checking a vehicle's history. Get a report instantly!
FAQ
Will an ultrasonic gauge measure over metal too?
You can measure nearly any common material using an ultrasonic gauge, including metals, plastics, fiberglass, ceramics, glass, etc.
Why do repainted panels read higher than factory paint?
Higher readings indicate thicker paint levels, suggesting the car may have received a paint job after leaving the factory (e.g., due to some paint damage or prior accidents).
Why measure paint thickness?
Measuring paint thickness helps evaluate paint quality, detect repairs or inconsistencies, ensure adherence to manufacturer specifications, extending a vehicle’s lifespan and preserving its resale value.