Table of Contents
- Energy consumption of electric cars
- Factors that affect energy consumption
- Battery size and efficiency
- Powertrain efficiency
- What type of charger to use?
- Tips to lower electricity consumption
- Drive efficiently and use regenerative braking
- Reduce your vehicle's weight
- Use eco-mode
- Maintain your battery
- Plan your routes
How much electricity does an electric car consume?
Learning about the energy consumption and charging expenses of an electric car can give you valuable insights into a vehicle's estimated range and maintenance costs.
How long does it take to charge an average EV, and what factors impact the charging speed? This article will answer all the questions that you may have.
Afraid of buying a wreck?
Check any VIN to learn a vehicle's history!
Energy consumption of electric cars
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) uses standardised tests to measure the energy consumption and estimated fuel efficiency of electric cars. These tests simulate different driving conditions and provide estimates of a car's energy consumption in miles per gallon of gasoline-equivalent (MPGe)
However, manufacturers also use different metrics, such as kWh/100 miles, miles/kWh or kWh/100 km. The former measures the energy in kilowatt-hours required to power a vehicle for 100 miles, (or 100 km) the latter – how many miles (or kilometers) a car can travel on one kilowatt-hour of energy.
While the EPA tests suggest that the best electric cars can drive up to 400 or 500 miles (640 to 800 km) on a single charge, real-world range is often lower. This is because electric vehicles are susceptible to driving and weather conditions, which can cause a significant reduction in range.
Factors that affect energy consumption

Battery capacity, driving habits, and weather conditions all play a role in determining how much energy your electric car uses. The average consumption increases even if you turn on air conditioning or a heat pump.
Battery size and efficiency
The battery size is a critical factor affecting the energy consumption of EVs. A larger battery typically means a longer driving range, as a vehicle can store more energy to power the electric motor. However, a larger battery also means more weight, reducing a car's overall efficiency and increasing energy consumption.
Additionally, the size of a battery affects the time it takes to charge a car. It takes longer to fully charge a larger battery, and this charging time can vary depending on the charging method.
Fast-charging stations can charge a battery faster but can also cause more significant battery degradation over time.
Powertrain efficiency
The powertrain of a vehicle transfers energy from the battery to the wheels, and a powertrain with higher efficiency requires less energy to convert the stored energy in the battery into mechanical energy for propelling a car.
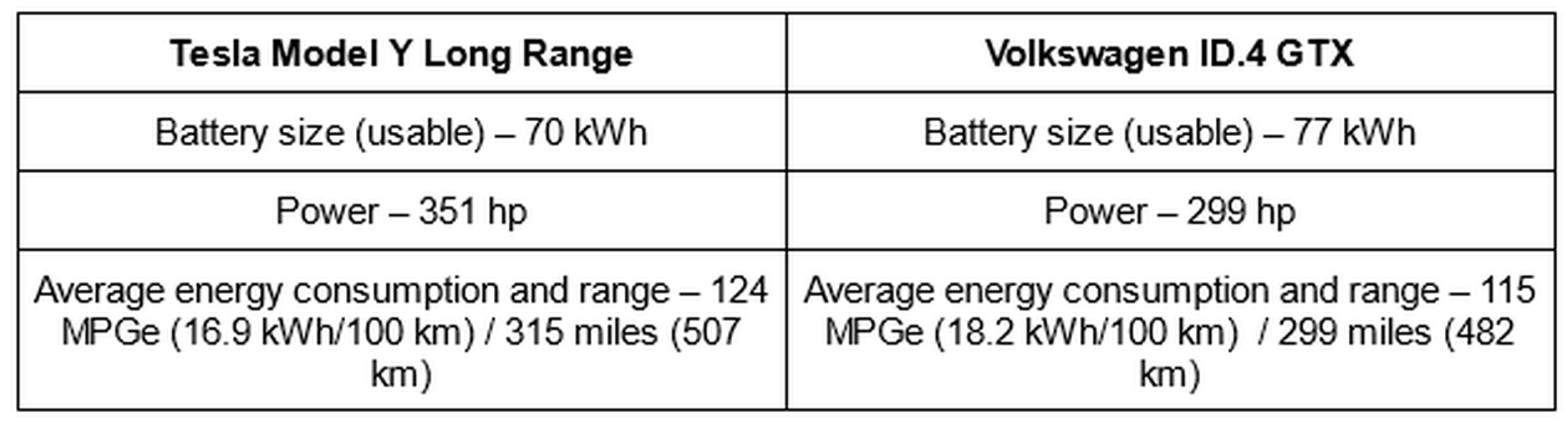
The type of motor used, transmission design, and the regenerative braking system also impact powertrain efficiency. The following comparison of the Tesla Model Y and the Volkswagen ID.4 GTX is an excellent example of powertrain efficiency. Although the Tesla Model Y has a smaller battery pack than the Volkswagen, its highly efficient battery cells, aerodynamic design, and relatively lighter body allow it to travel longer distances on a single charge.
What type of charger to use?

When it comes to charging electric cars, there are three main types of chargers to consider, each with its unique level of charging power:
- Level 1 chargers. These chargers use a standard 120-volt outlet and are typically the slowest type of charging, with a peak charging power of around 2.4 kW. It means that if you want to charge a car like the Ford Mustang Mach-e, which has a 75 kWh battery pack, it will take approximately 54 hours to recharge the battery from 0 to 100%.
- Level 2 chargers. These chargers require a 240-volt outlet and can provide a faster charging speed than Level 1 chargers. They have a peak charging power of around 19 kW and can charge a car with a smaller battery size in around 4-8 hours.
- DC fast chargers. These chargers are the fastest type of charging, and are commonly found in public charging stations along highways and major routes. They require a special connector, providing a peak charging power from around 50 kW to 350 kW. DC fast chargers can charge a car with a smaller battery size in as little as 30 minutes but are more expensive to use.
Tips to lower electricity consumption
If you own an electric car, you’re already enjoying the benefits of eco-friendly and cost-efficient transportation. Nonetheless, there are further tactics you can adopt to enhance energy efficiency and reap even greater benefits.
Drive efficiently and use regenerative braking
One of the most effective ways to lower your electric car's energy consumption is to drive efficiently by maintaining a steady speed and avoiding sudden acceleration or braking.
Additionally, use regenerative braking whenever possible by taking your foot off the accelerator and allowing your car to slow down naturally. This will help to capture the energy that would otherwise be lost during braking and use it to recharge your car's battery, increasing its efficiency and reducing energy consumption.
Reduce your vehicle's weight
Another tip to lower your electric car's energy consumption is to reduce your vehicle's weight by removing any unnecessary items from the trunk, such as heavy equipment or extra luggage.
Use eco-mode
Using eco-mode is another effective way to lower your electric car's energy consumption. Eco-mode typically adjusts a car's acceleration, climate control, and other settings to reduce energy usage.
It can also limit a car's top speed, helping to conserve energy when driving at higher speeds. By using eco-mode, you can significantly reduce your electric car's energy consumption, allowing you to travel further on a single charge.
Maintain your battery
Maintaining your battery is crucial for optimizing your electric car's energy consumption. Here are some examples of how you can do it:
- Charge your battery regularly. To prevent your battery from fully discharging, it's recommended to charge it regularly, ideally before it reaches a low charge level. Try to keep your battery at around 50% to 80% charge level.
- Avoid exposing your battery to extreme temperatures. High temperatures can cause your battery to degrade faster, so try to avoid leaving your electric car parked in direct sunlight for extended periods. Cold temperatures can also reduce the battery's performance, so park your EV in a garage or a covered area during winter.
- Store your battery properly. If you need to store your electric car for an extended period, make sure to follow the manufacturer's guidelines for battery storage. This may include keeping the battery at a specific charge level and temperature in a dry and cool environment.
Plan your routes
Planning your routes can also help to lower your electric car's energy consumption. By choosing the most efficient routes and avoiding unnecessary detours, you can reduce the distance you need to travel and save energy in the process.
- Use apps or online tools. There are many apps and online tools available that can help you plan the most efficient routes for your electric car. These tools can provide real-time traffic updates and other helpful information to save time and energy.
- Plan your charging stops. To ensure that you always have enough charge to reach your destination, plan your charging stops in advance. This can help you avoid running out of charge and making unexpected stops.
Electric vehicles may require more attention and planning to achieve maximum efficiency, but the benefits of reduced energy consumption and lower operating costs make it worth the effort.
By adopting these energy-saving tips and making them part of your driving habits, you can enjoy the full benefits of owning an electric car.

Check your VIN
Avoid costly problems by checking a vehicle's history. Get a report instantly!
FAQ
How much electricity do you need to charge an electric car?
Fully charging a 60 kWh battery requires 60 kWh of electricity, but energy loss during charging, such as AC-DC conversion inefficiency, can increase electricity consumption by up to 10%.
How to lower electricity consumption when charging a car?
Lower your electric car charging costs by charging off-peak, using a smart charger, avoiding overcharging, and maintaining your battery.
How much electricity does an EV home charger use?
A Level 1 EV charger uses a standard household 120V outlet and uses up to 2.4 kW of power. A Level 2 charger requires a 240V circuit and uses up to 7.4 kW, depending on the car's charging capacity.